DLP projectors have been around for a while, but not many people know how they work or how they compare to other technologies. I’ve had my fair share of experience with DLP projectors, and let me tell you, they’re more than just a fancy piece of tech.
So, if you’re in the market for a new projector or just curious about how DLP projectors work, keep reading!
Here is a list of some popular DLP projector models:
- Optoma HD39HDR – A 1080p projector that’s great for gaming and home entertainment.
- BenQ HT2150ST – A short-throw projector that’s ideal for small rooms or home theaters.
- ViewSonic PX747-4K – A 4K projector that offers stunning image quality and HDR compatibility.
- LG PF50KA – A portable projector that’s great for on-the-go use and outdoor movie nights.
- Acer H6531BD – A budget-friendly option that offers Full HD resolution and a 10,000:1 contrast ratio.
What is a DLP Projector?
First things first, what is a DLP projector? DLP stands for Digital Light Processing, and it’s a technology developed by Texas Instruments. Unlike LCD projectors that use liquid crystals to project an image, DLP projectors use tiny mirrors to reflect light onto a screen.
These mirrors are so small that you can fit over two million of them on a single DLP chip.
Here is a list of the most popular projector technologies in the market:
- DLP (Digital Light Processing) – Uses tiny mirrors to reflect light onto the screen. DLP projectors offer excellent contrast and deep blacks, but can suffer from the “rainbow effect”.
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) – Uses liquid crystals to manipulate light and produce an image. LCD projectors offer bright, vibrant colors, but can have lower contrast than other technologies.
- LCoS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon) – Similar to LCD, but uses a reflective layer of silicon instead of glass. LCoS projectors offer high contrast and deep blacks but can be more expensive than other technologies.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode) – Uses LEDs to produce light instead of a traditional lamp. LED projectors can be more energy-efficient and offer longer lamp life, but may not be as bright as other technologies.
- Laser – Uses lasers to produce light instead of a traditional lamp. Laser projectors offer high brightness, excellent color accuracy, and long lamp life, but can be more expensive than other technologies.
How Do DLP Projectors Work?
So, how exactly do these tiny mirrors work? Well, each mirror corresponds to a pixel in the projected image. When the mirror tilts towards the light source, it reflects light onto the screen. When the mirror tilts away from the light source, it reflects light away from the screen. By rapidly tilting the mirrors on and off, the DLP chip can create the illusion of a moving image.
Compared to other projector technologies like LCD and LCoS, DLP projectors have a few advantages. For one, they’re known for their excellent contrast ratio and deep blacks. This is because the mirrors on the DLP chip can completely block light from the light source when they’ve tilted away from it.
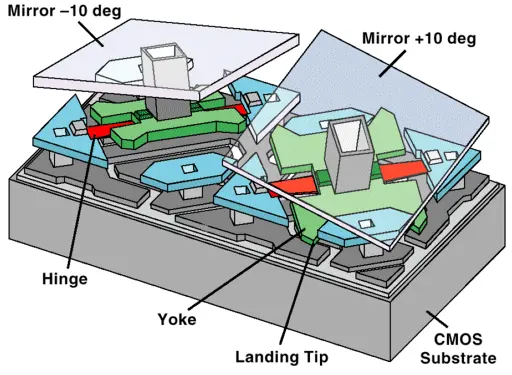
DMD stands for Digital Micromirror Device, which is a key component of DLP projectors that contains thousands of tiny mirrors that reflect light onto the screen to produce an image.
DLP projectors also tend to be more affordable than LCoS projectors, and they don’t suffer from the screen-door effect that LCD projectors sometimes do.
But, it’s not all sunshine and rainbows with DLP projectors. One downside is that they can suffer from the rainbow effect. This is a visual artifact where some people see rainbow-like flashes of color in high-contrast images. This effect is caused by the way DLP projectors create color.
Color in DLP Projectors
To create color, DLP projectors use a color wheel that spins rapidly in front of the light source. The color wheel is divided into three sections, one for red, green, and blue. As the wheel spins, different colors are projected onto the DLP chip. The mirrors then reflect these colors onto the screen to create a full-color image.
The downside to this color-wheel system is that it can lead to the rainbow effect. Some people are more sensitive to this effect than others, so it’s worth keeping in mind if you’re considering a DLP projector.
Short-Throw Projectors
Short-throw projectors are a type of projector that can display a large image from a short distance away. They’re a great option for smaller rooms or home theaters where space is limited.
Unlike traditional projectors, which need to be placed several feet away from the screen or wall, short-throw projectors can be placed just a few feet away and still produce a large, high-quality image.
This can be a real game-changer for people who want to create a home theater experience in a smaller space. If you’re considering a short throw projector, be sure to pay attention to the throw ratio, which determines how far away the projector needs to be in order to produce a certain size image.
With a short-throw projector, you can enjoy a big-screen experience without having to rearrange your entire living room!
Projector’s Interface and Operating System
When it comes to projectors, there are a variety of interface and operating system options to choose from. Some projectors come with built-in interfaces like HDMI, USB, and Ethernet, while others may require additional adapters or dongles.
In terms of operating systems, some projectors may come with their own proprietary operating system, while others may be compatible with popular operating systems like Windows, Mac OS, or Android.
The operating system you choose may affect the types of apps and software you can use with your projector, as well as the overall user experience. For example, projectors that run Android may offer access to popular streaming apps like Netflix and Hulu, while projectors that run Windows may be better suited for business or education applications.
When choosing a projector, be sure to consider your interface and operating system needs, and make sure the projector you choose is compatible with your devices and preferred software.
Tips and Tricks for Using a DLP Projector
If you do decide to go with a DLP projector, there are a few tips and tricks you should keep in mind. First, make sure you have a good-quality screen. DLP projectors are known for their deep blacks, but that effect is lost if you project onto a low-quality screen. Invest in a good screen, and you’ll see a noticeable improvement in image quality.
Another tip is to pay attention to the lamp life of your DLP projector. DLP projectors use a lamp as their light source, and these lamps can be expensive to replace. Make sure you’re getting a projector with a decent lamp life, and try to use eco-mode when you can extend the life of the lamp.
Finally, if you’re sensitive to the rainbow effect, try to get a DLP projector with a faster color wheel. Faster color wheels can help reduce the visibility of the effect.
Conclusion
DLP projectors are a fantastic choice for anyone looking for an affordable and high-quality projector. They offer excellent contrast and deep blacks, and they’re more affordable than some other projector technologies. However, they do suffer from the rainbow effect, which can be a downside for some people.
At the end of the day, choosing a projector comes down to your personal preferences and needs. But, if you’re considering a DLP projector, don’t let the rainbow effect scare you off. With a good-quality screen and some attention to lamp life, you can enjoy a high-quality viewing experience with a DLP projector.
So, there you have it, folks! A quick rundown on how DLP projectors work and how they compare to other technologies.





