Are you ready to learn about the benefits and downsides of hydrogen-powered cars? How do they compare with electric vehicles and which technology is more sustainable?
First, let’s see a full picture of hydrogen-powered cars and dive into this interesting technology.
What are Hydrogen-Powered Cars?
Hydrogen-powered cars, also known as fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), use hydrogen gas to power an electric motor. The process begins by converting hydrogen gas into electricity through a fuel cell stack.
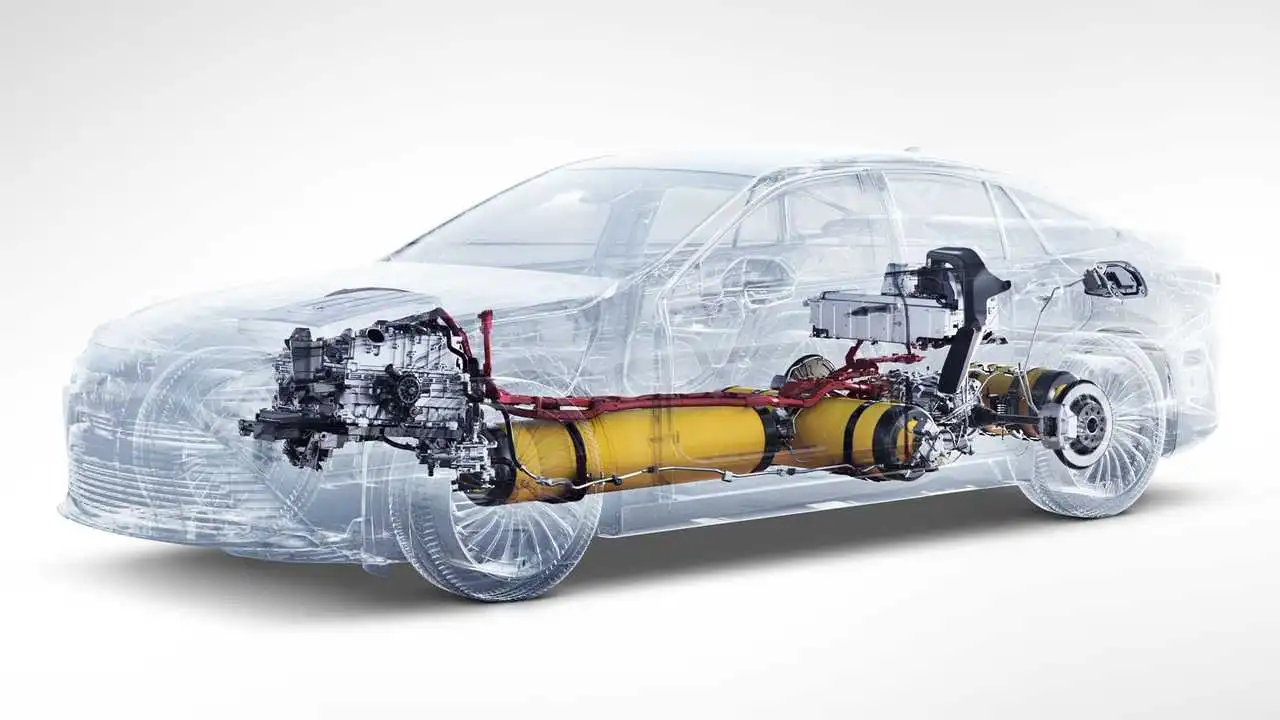

This electricity is then used to power the car’s electric motor, which drives the wheels. And the best part? The only byproduct is water vapor, making it a much cleaner alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
What Engine Type is Used?
Unlike traditional gas-powered engines that use explosions to power the car, hydrogen-powered cars use fuel cells to convert hydrogen into electricity. This means that they don’t have any moving parts, making them much quieter and smoother to drive.
Plus, the electric motor provides instant torque, making them great for accelerating quickly.
There is also another 4-stroke engine, the same as the petrol one. Instead of injecting fuel + oxygen, it injects hydrogen and oxygen. The engine makes the same noise as the former ones. The emissions in this case close to zero.
What are Hydrogen Power Cells?
Hydrogen power cells are the heart of a hydrogen-powered car. They’re made up of two electrodes with an electrolyte solution in between them. When hydrogen gas is passed over the anode, it splits into protons and electrons. The electrons travel through a wire to the cathode, creating an electric current.
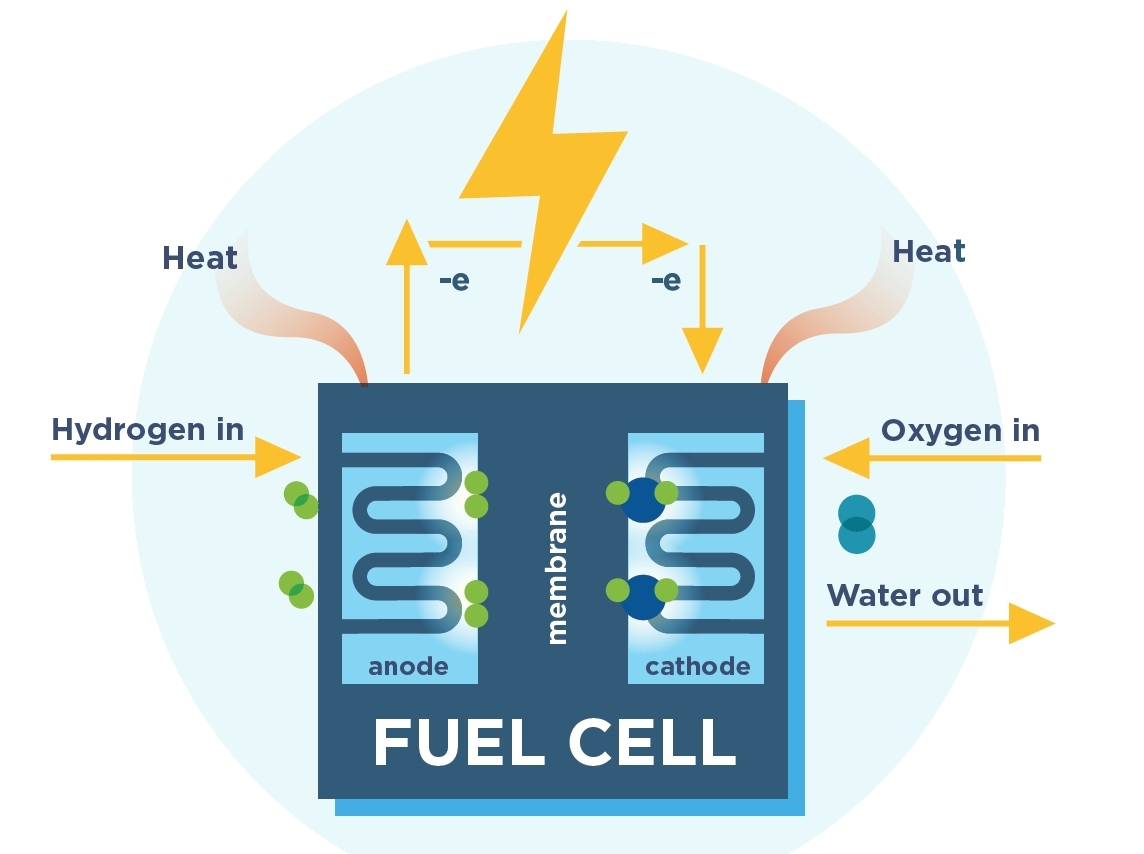
The protons pass through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they combine with oxygen from the air to create water vapor.
How do Hydrogen-Powered Cars Compare to Electric Ones?
Hydrogen-powered cars have a few advantages over electric cars. For starters, they have a longer range and can be refueled in just a few minutes, making them more convenient for long road trips.
They also don’t require as much battery storage, which can be expensive and heavy. However, electric cars are still more widely available and have more infrastructure for charging stations.
How is Hydrogen Produced?
There are several methods for producing hydrogen, but the most common method is through a process called steam methane reforming. In this process, natural gas (which is primarily methane) is mixed with steam and heated in the presence of a catalyst, causing a chemical reaction that produces hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is then separated from the hydrogen through a process called pressure swing adsorption, leaving pure hydrogen gas.
Another method for producing hydrogen is through electrolysis, in which an electric current is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. This process requires a significant amount of electricity, which is typically generated from renewable sources like solar or wind power to ensure a low carbon footprint.
A third method for producing hydrogen is through biomass gasification, in which organic materials like wood chips or agricultural waste are heated in the presence of steam to produce a gas mixture containing hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases. The hydrogen is then separated from the other gases through a process called gas cleanup.
Regardless of the method used, producing hydrogen can be energy-intensive and may involve significant greenhouse gas emissions.
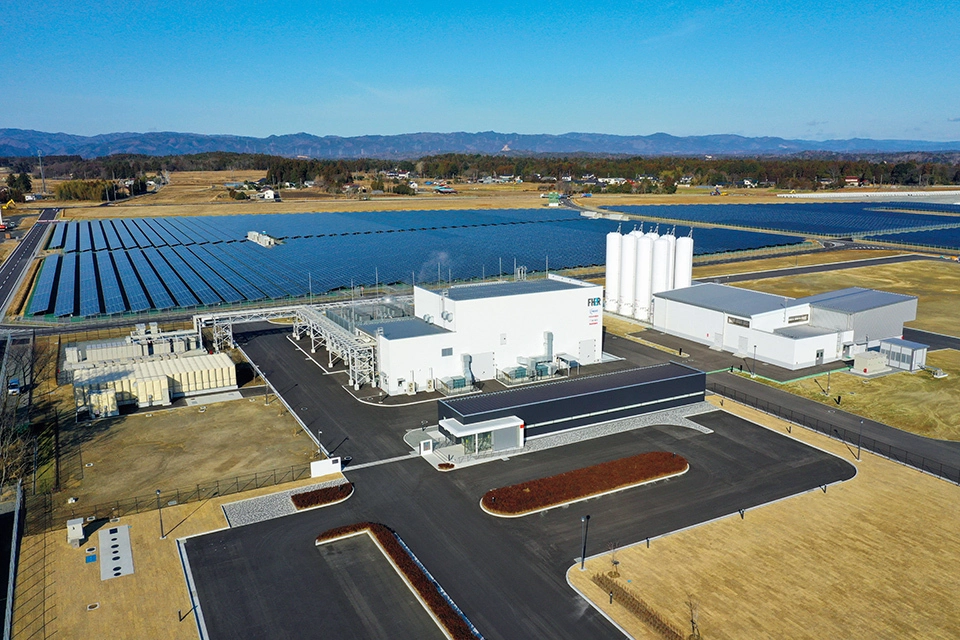

The Fukushima Hydrogen production plant is the world’s largest. As can be seen in the image above, it uses vast surfaces of solar panels. To learn more check out this article The World’s Largest Hydrogen-Production Facility.
How are Lithium Batteries Produced?
Lithium batteries are typically produced in a multi-step process that involves several chemical reactions and high-temperature processing. The first step is the extraction of lithium from lithium-rich ores. This can be done through a variety of methods such as brine mining or hard rock mining. The extracted lithium is then processed into a usable form, typically lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide.
The production of lithium batteries for cars can have significant environmental impacts, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and water use. The extraction of lithium from ores can involve the use of large amounts of water, and can also result in the contamination of groundwater and surface water with chemicals and heavy metals. The processing of lithium can also generate significant greenhouse gas emissions, particularly if fossil fuels are used to power the manufacturing process.
In addition, the production of cathode materials like cobalt can involve hazardous working conditions and environmental pollution. Particularly in countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo where much of the world’s cobalt is sourced.
While the use of lithium batteries for electric vehicles can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality, it is important to consider the environmental impacts of their production and disposal.

To learn more about lithium extraction read this article: What Is Lithium Extraction and How Does It Work?
What is the Fuel Efficiency of Hydrogen-Powered Cars?
The fuel efficiency of hydrogen-powered cars is impressive, with some models achieving up to 60 miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe). This means that they can travel 60 miles on the energy equivalent of one gallon of gasoline.
Compare that to a traditional gas-powered car that might only get 25-30 miles per gallon, and you can see why hydrogen-powered cars are such an attractive option.
Benefits of Hydrogen-Powered Cars
- Zero Emissions: Hydrogen-powered cars produce zero harmful emissions, making them a cleaner and greener alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
- Fuel Efficiency: These cars are highly fuel-efficient and can achieve impressive MPGe ratings, resulting in lower fuel costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Quick Refueling: Hydrogen-powered cars can be refueled in just a few minutes, which is comparable to the time it takes to fill up a traditional gas-powered car.
- Longer Range: Hydrogen-powered cars have a longer range than electric cars, making them a better option for long road trips.
- Quieter and Smoother: Hydrogen-powered cars are much quieter and smoother to drive than traditional gas-powered cars, providing a more comfortable and enjoyable driving experience.
- Energy Security: Hydrogen can be produced domestically, reducing dependence on foreign oil and increasing energy security.
Downsides of Hydrogen-Powered Cars
- Limited Infrastructure: There are currently limited refueling stations for hydrogen-powered cars, making it difficult for drivers to find a place to refuel.
- High Cost: Hydrogen-powered cars are currently more expensive than traditional gas-powered cars or even electric cars, making them less accessible to many consumers.
- Safety Concerns: Hydrogen gas is highly flammable and requires special storage and handling, which can raise safety concerns.
- Production Challenges: The production of hydrogen gas requires a significant amount of energy, which can be a challenge to produce sustainably and economically.
- Technological Development: Hydrogen-powered cars are still a relatively new technology, and there is still much to be learned and improved upon before they become mainstream options.
- Limited Availability: Hydrogen-powered cars are not yet widely available, with only a few models on the market and limited availability in certain regions.
Electric Vehicles vs. Hydrogen-Powered Cars: Which is More Sustainable?
The debate over which are more sustainable, electric vehicles or hydrogen-powered cars, has been ongoing for years. Let’s take a closer look at the arguments for both sides.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles are powered by batteries that store electricity from the grid or other renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. Here are some of the arguments for EVs being the more sustainable option:
- Low Emissions: EVs produce zero emissions when driving, making them a cleaner alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
- Improving Grid: As renewable energy sources become more widespread and the electric grid becomes cleaner, EVs will become even more sustainable as they rely on electricity from these sources.
- Recycling: EV batteries can be recycled at the end of their life, reducing waste and the need for new materials.
- More Accessible: EVs are becoming more accessible and affordable as production costs decrease and more models become available.
To learn more read our article on The Advantages Of Electric Vehicles.
Hydrogen-Powered Cars
Hydrogen-powered cars use hydrogen gas to power an electric motor. The hydrogen gas is stored in high-pressure tanks, and the fuel cell stack converts the hydrogen into electricity. Here are some of the arguments for hydrogen-powered cars being the more sustainable option:
- Domestic Production: Hydrogen can be produced domestically, reducing dependence on foreign oil and increasing energy security.
- Zero Emissions: Hydrogen-powered cars produce zero emissions, making them a cleaner alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
- Quick Refueling: Hydrogen-powered cars can be refueled in just a few minutes, which is comparable to the time it takes to fill up a traditional gas-powered car.
- Longer Range: Hydrogen-powered cars have a longer range than electric cars, making them a better option for long road trips.
So, which is more sustainable?
The answer is not straightforward. Both EVs and hydrogen-powered cars have their advantages and disadvantages when it comes to sustainability. However, at the moment, EVs are considered to be the more sustainable option overall.
This is because the electric grid is becoming cleaner and more renewable sources are being used to produce electricity, whereas producing hydrogen gas requires a significant amount of energy.
Additionally, EVs are more widely available and accessible than hydrogen-powered cars, which are still a relatively new technology with limited availability.
In conclusion, both EVs and hydrogen-powered cars have the potential to be more sustainable options for transportation in the future. However, at this point, EVs are considered to be the more sustainable option due to their wider availability and the improving sustainability of the electric grid.
Car Manufacturers Investing in Hydrogen-Powered Cars
While electric vehicles have been receiving the bulk of the attention in the world of sustainable transportation, several car manufacturers are investing heavily in hydrogen-powered cars as well.
Here are some of the major players in the hydrogen car market:
- Toyota: Toyota has been a pioneer in the hydrogen-powered car market with its Mirai model, which has been on the market since 2014. Toyota has continued to invest in hydrogen fuel cell technology and plans to release new hydrogen-powered models in the coming years.
- Hyundai: Hyundai has also been a leader in the hydrogen car market with its Nexo model, which has a range of over 400 miles on a single tank of hydrogen. Hyundai plans to invest $7.4 billion in hydrogen fuel cell technology by 2025.
- Honda: Honda has been developing hydrogen fuel cell technology for over two decades and has released the Clarity Fuel Cell vehicle. The Clarity has a range of 360 miles on a single tank of hydrogen.
- General Motors: General Motors has announced plans to release a new hydrogen-powered SUV in 2024. The vehicle will be built on a new platform specifically designed for electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles.
These car manufacturers are betting on hydrogen fuel cell technology as a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
The Downsides of Producing, Transporting, and Storing Hydrogen
While hydrogen-powered cars have the potential to be a more sustainable form of transportation, there are several downsides to producing, transporting, and storing hydrogen that needs to be considered.
- Production: Hydrogen is primarily produced through a process called steam methane reforming, which requires large amounts of natural gas. This means that the production of hydrogen is not entirely emissions-free and could contribute to climate change.
- Transportation: Hydrogen is not as dense as gasoline or diesel, which means that it requires more space to transport the same amount of energy. This can make transporting hydrogen more expensive and less efficient than transporting traditional fuels.
- Storage: Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas that requires specialized tanks for storage. These tanks can be expensive and heavy, which can add to the overall cost and weight of hydrogen-powered cars.
- Infrastructure: There are currently very few hydrogen refueling stations available, which limits the range of hydrogen-powered cars. Building out the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling would require significant investment and could take years to complete.
- Energy Loss: The process of converting energy into hydrogen, transporting it, and then converting it back into electricity to power a car results in significant energy loss. This means that hydrogen-powered cars are less efficient than electric cars.
- Safety: Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas that can be dangerous if not handled properly. There have been concerns about the safety of storing and transporting large amounts of hydrogen.
These downsides show that while hydrogen-powered cars have the potential to be a sustainable form of transportation, there are significant challenges that need to be addressed. In the meantime, electric cars may be a more practical and efficient solution for reducing emissions from transportation.
The Downsides of Producing Lithium Batteries for EVs
While electric vehicles (EVs) are often seen as a more sustainable form of transportation, the production of lithium-ion batteries that power these vehicles comes with several downsides.
- Resource Extraction: The production of lithium batteries requires the extraction of rare earth metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The mining of these metals can have significant environmental impacts, including deforestation, water pollution, and habitat destruction.
- Energy Intensive: The production of lithium batteries is an energy-intensive process that requires significant amounts of electricity. This means that the production of lithium batteries contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
- Limited Lifespan: While lithium batteries have a longer lifespan than traditional lead-acid batteries, they still degrade over time and need to be replaced. The disposal of these batteries can have environmental impacts if not handled properly.
- Recycling Challenges: While lithium batteries are recyclable, the process of recycling them is expensive and not yet widely available. This means that many lithium batteries end up in landfills, where they can have environmental impacts.
- Cost: The production of lithium batteries is expensive, which can add to the overall cost of EVs. This can make them less accessible to consumers and limit their adoption.
- Safety: Lithium batteries are flammable and can catch fire if damaged or exposed to extreme temperatures. While rare, these incidents can have significant safety implications.
As technology advances, efforts are being made to address these challenges, including improving battery recycling and reducing the number of rare earth metals needed in battery production.
The efficiency of Electric Vehicles vs Hydrogen-Powered Ones
- Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles: The overall efficiency of hydrogen-powered vehicles is typically around 30-40%. Around 30-40% of the energy input is converted into usable energy for the vehicle. The remaining 60-70% is lost as heat and through other system losses.
- EVs: The overall efficiency of EVs is typically around 80-90%. Around 80-90% of the energy input is converted into usable energy for the vehicle. The remaining 10-20% is lost as heat and through other system losses.
When it comes to overall efficiency, EVs have the edge over hydrogen-powered vehicles.
However, it’s important to note that hydrogen-powered vehicles have some advantages over EVs, such as faster refueling times and longer driving ranges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both hydrogen-powered vehicles and EVs represent promising alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered cars. With their improved environmental performance and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
Hydrogen-powered vehicles offer some key advantages over EVs, including faster refueling times and longer driving ranges. However, they face significant challenges when it comes to the production, storage, and transportation of hydrogen, which can be costly and energy-intensive. In addition, the overall efficiency of the energy conversion process in hydrogen-powered vehicles is lower than that of EVs, meaning that more energy is lost as heat and through other system losses.
On the other hand, EVs offer higher overall energy efficiency, meaning that more of the energy input is converted into usable energy for the vehicle. They also have the advantage of being able to take advantage of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, for charging. However, they face challenges when it comes to battery production, which can be resource-intensive and may involve environmentally harmful processes.
When it comes to car makers, several major companies, including Toyota, Honda, and Hyundai, have invested heavily in hydrogen fuel cell technology and are actively producing hydrogen-powered vehicles. However, other companies, such as Tesla and GM, have focused primarily on EVs.
In any case, it’s clear that reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and transitioning to cleaner forms of transportation will be essential in mitigating the impacts of climate change and ensuring a sustainable future.
Thanks for reading!
Reference
Hydrogen vehicle – Wikipedia. Link to the source.





