Neptune is the eighth and most distant planet from the sun. It is also one of the most mysterious and fascinating worlds in our solar system.
But how far is Neptune from Earth? And what makes it so intriguing? In this article, we will explore these questions and more.
The Distance Between Neptune and Earth
The distance between Neptune and Earth is constantly changing, depending on where they are in their orbits around the sun. Both planets follow elliptical paths that bring them closer or farther away from the sun at different times.
When Neptune and Earth are on the same side of the sun, at their closest point, they are only 2.7 billion miles (4.3 billion kilometers) apart. That’s about 30 times the distance between Earth and the sun.
But when they are on opposite sides of the sun, at their farthest point, they can be as much as 2.9 billion miles (4.7 billion kilometers) apart. That’s about 32 times the distance between Earth and the sun.
To put these numbers into perspective, it would take a spacecraft traveling at 10 miles per second (16 kilometers per second) about 12 years to reach Neptune from Earth at its closest point, and about 13 years at its farthest point.
The Discovery of Neptune
Neptune was not discovered by looking through a telescope, but by using mathematics. In the early 1800s, astronomers noticed that Uranus, which had been discovered in 1781 by William Herschel, had some irregularities in its orbit that could not be explained by Newton’s laws of gravity.
Two mathematicians, John Couch Adams in England and Urbain Le Verrier in France, independently calculated that there must be another planet beyond Uranus that was affecting its motion. They predicted where this planet should be in the sky based on their calculations.
In 1846, a German astronomer named Johann Gottfried Galle used Le Verrier’s predictions to find Neptune with a telescope for the first time. He found it within one degree of where Le Verrier had said it would be. Adams had also sent his predictions to other astronomers earlier that year, but they were ignored or delayed.
Both Adams and Le Verrier are credited with discovering Neptune today.
The Features of Neptune
Neptune is a gas giant planet with no solid surface. It has a thick atmosphere made mostly of hydrogen and helium, with traces of methane that give it a blue-green color. It has four rings made of dust and ice particles that orbit around it.
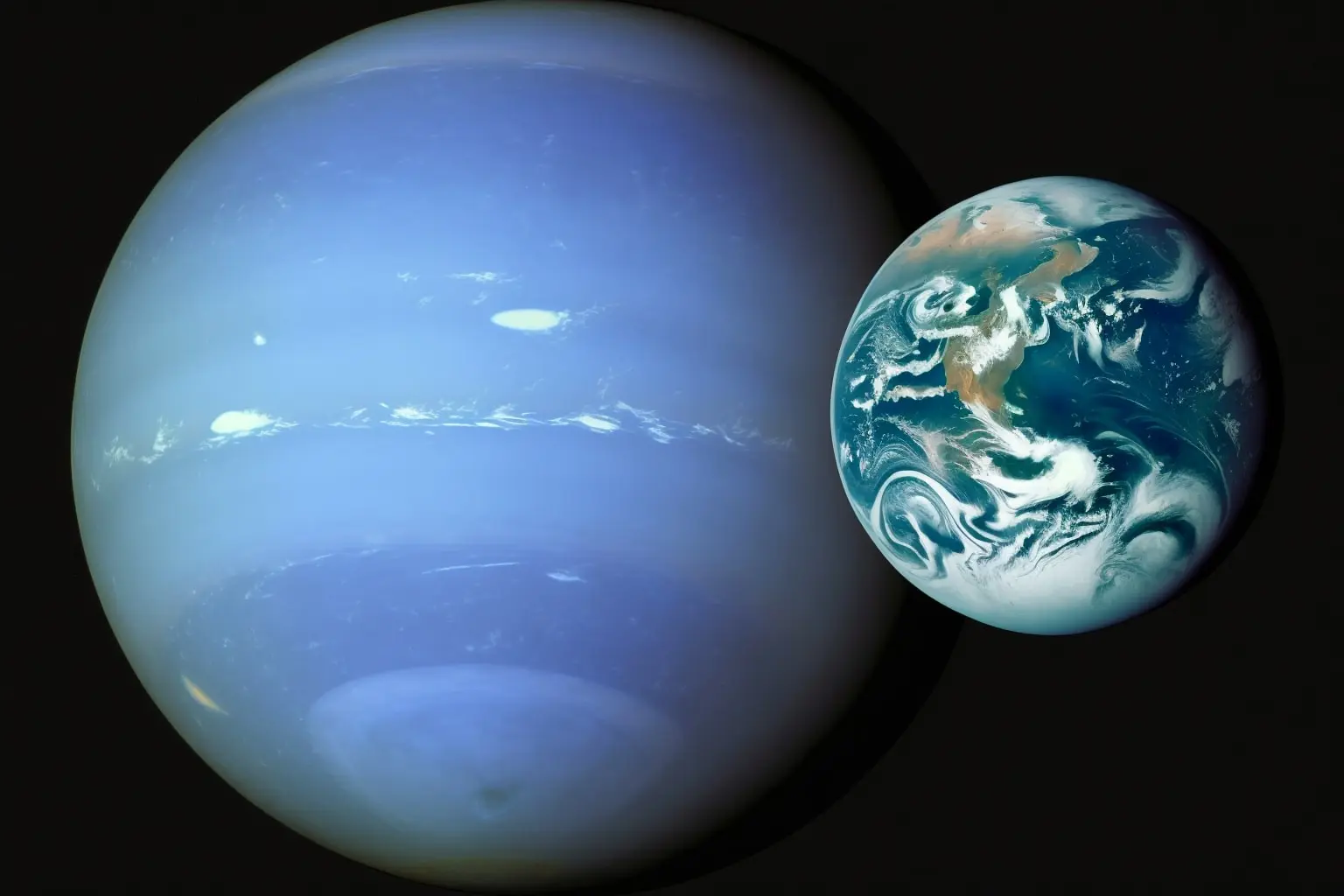

The diameter of Neptune is approximately 49,244 kilometers (30,775 miles). In comparison, the diameter of Earth is approximately 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles). Therefore, Neptune’s diameter is about 3.9 times larger than Earth’s diameter.
Neptune has 13 known moons, some of which are very unusual. The largest moon is Triton, which orbits Neptune in a retrograde direction (opposite to its rotation). Triton has a thin atmosphere of nitrogen and methane ice volcanoes that spew out plumes of gas and dust.
Another moon is Nereid, which has one of the most eccentric orbits in our solar system. It can get as close as 840 thousand miles (1.4 million kilometers) or as far as 5 million miles (8 million kilometers) from Neptune during its orbit.
Here is a list of all known moons that orbit Neptune:
- Naiad
- Thalassa
- Despina
- Galatea
- Larissa
- Proteus
- Triton
- Nereid
- Halimede
- Sao
- Laomedeia
- Psamathe
- Neso (most recently discovered in 2002)
Want to learn more and see them live, check out this other article on NASA’s Live Solar System Explorer.
Neptune’s Magnetic Field
Neptune also has a powerful magnetic field that is tilted by about 47 degrees from its axis of rotation. This causes intense auroras (northern and southern lights) near its poles.
Neptune is also known for its storms and winds that can reach up to 1 thousand miles per hour (1.6 thousand kilometers per hour). The most famous storm on Neptune is called the Great Dark Spot, which was first seen by Voyager 2 spacecraft when it flew by Neptune in 1989.
The Great Dark Spot was a huge storm system about twice as big as Earth that lasted for several years before disappearing in 1994. Since then, other dark spots have appeared and vanished on Neptune’s surface.
The Future of Neptune Exploration
Neptune is a challenging planet to explore because of its great distance and harsh environment. It takes a lot of time, money, and technology to send a spacecraft there and communicate with it.
However, many scientists and engineers are interested in Neptune and its moons because they offer unique insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system and other planetary systems.
There are several proposals for future missions to Neptune that could launch in the next few decades. Some of them are:
- Trident: A NASA mission that would fly by Neptune and Triton in 2038. It would study their atmospheres, magnetospheres, geology, and history.
- ODINUS: A European mission that would send two orbiters to Uranus and Neptune in 2034. It would investigate their structure, dynamics, weather, rings, and moons.
- Ice Giants Orbiter: A NASA mission that would orbit either Uranus or Neptune in 2040. It would measure their gravity, magnetic fields, thermal emissions, and internal structure.
- Ice Giants Probe: A NASA mission that would send a probe into the atmosphere of either Uranus or Neptune in 2040. It would measure their temperature, pressure, composition, and winds.
These missions are still in the conceptual stage and have not been approved or funded yet. They face many technical challenges such as power generation, propulsion, navigation, communication, and radiation protection.
However, if they succeed they will reveal new wonders about Neptune and its fascinating moons.
To learn more about the latest space discoveries check out our article on 10 Mind Expanding Space Discoveries of Recent Years.
Neptune in Mythology
In Roman mythology, Neptune was the god of the sea, earthquakes, and horses. He was also known as the brother of Jupiter (Zeus in Greek mythology) and Pluto (Hades in Greek mythology) and was one of the twelve Olympian gods.
Neptune was typically depicted as a mature man with a long beard, holding a trident and riding a sea creature, often a hippocampus or a chariot pulled by sea horses. In Roman culture, he was worshipped as a patron of seafarers, fishermen, and anyone who worked on the water.
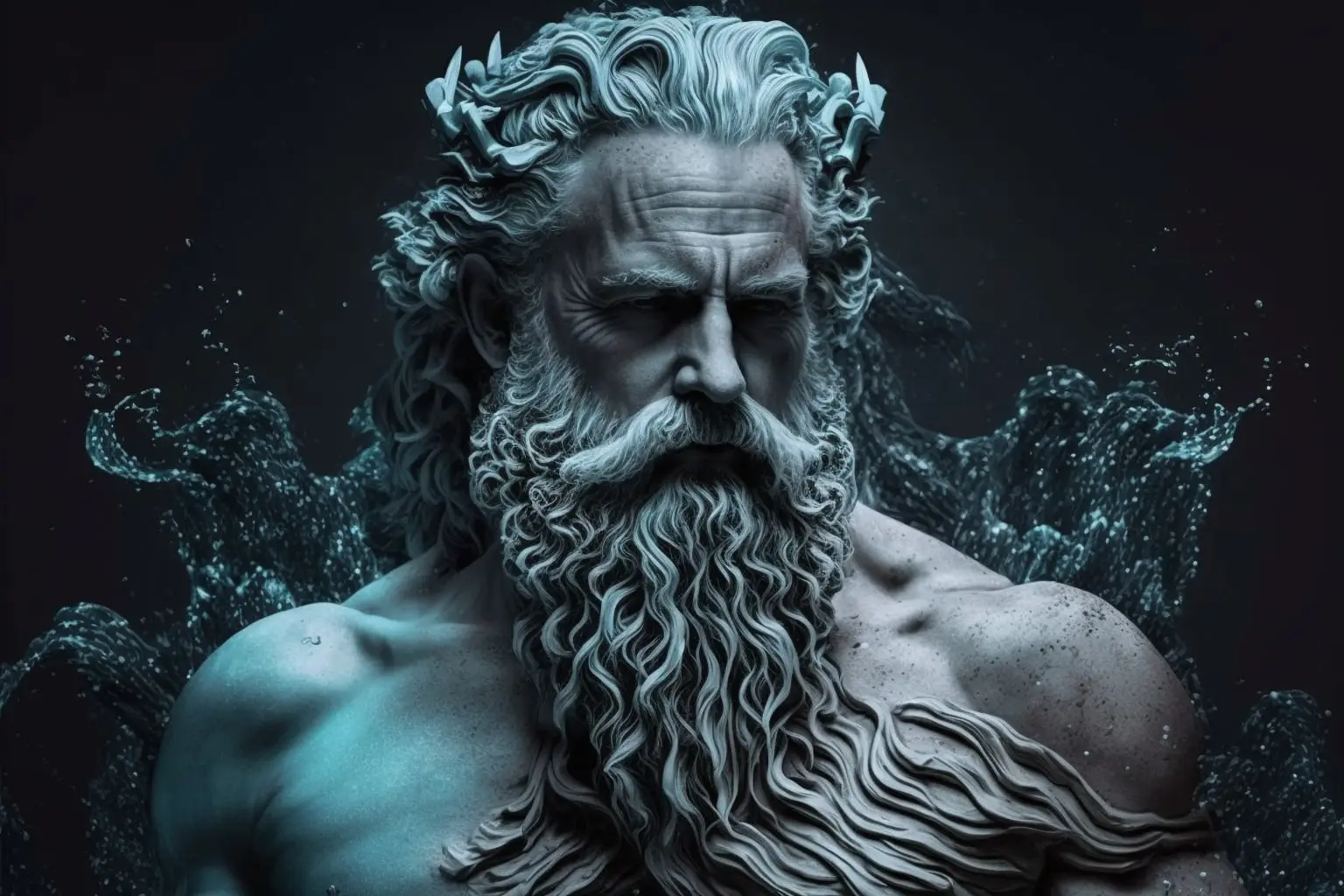

The planet Neptune was named after the god, following the tradition of naming planets after Roman deities.
Conclusion
Neptune is one of the most fascinating planets in our solar system, known for its beautiful blue hue and unique features. While it may be located far away from Earth, its distance is not an insurmountable obstacle to exploration and discovery.
Scientists and researchers have made incredible strides in understanding Neptune and its moons, and there is still much to be learned in the years to come. Whether you are an astronomy enthusiast or simply curious about the wonders of our universe, exploring the mysteries of Neptune is a journey worth taking.
So, the next time you gaze up at the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the vastness of our solar system and the incredible planet that is Neptune, millions of miles away.
References
How Far Away is Neptune? Space.com. Link to the resource
How Far Is Neptune From The Sun & Earth? – Journalofcosmology.com. Link to the resource